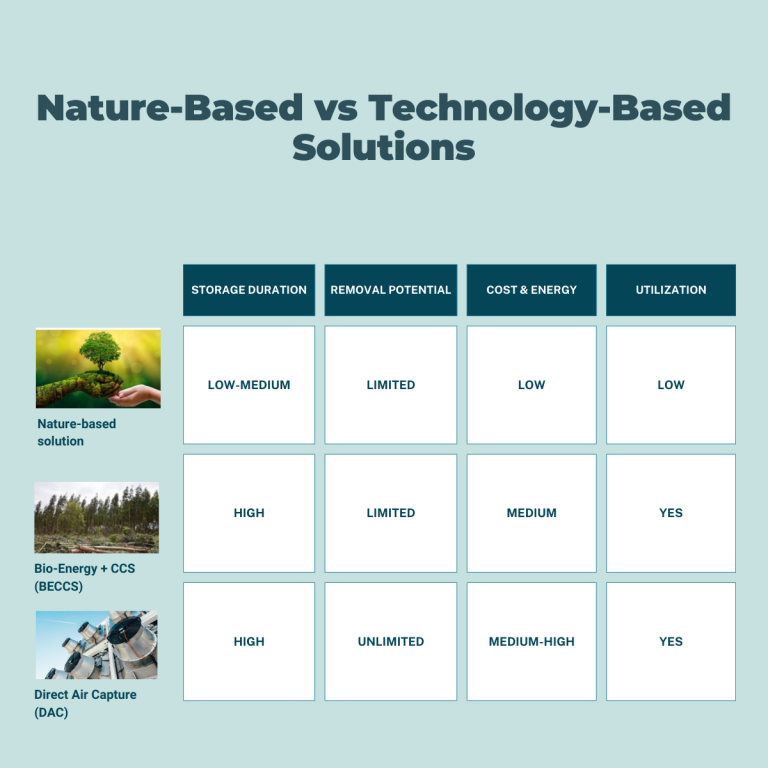
There are several ways of removing carbon from the atmosphere, they can be distributed in two main categories: technology-based and nature-based solutions. Both methods have their different ways of capturing CO₂ at different scale and cost.
Direct Air Capture (DAC) is one example of technology-based carbon removal. Check out our previous posts to learn more about DAC!
Another carbon removal solution is Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS). This involves capturing and permanently storing CO₂ from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. Because plants absorb CO₂ as they grow, this is a way of removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.
Both technological solutions are scalable, and measuring how much carbon has been captured in the process is relatively easy. Although both industries have great potential, they still need to take steps in scaling up and reducing their energy consumption.
Nature-based carbon removal has lower costs compared to technology-based solutions. This method involves natural solutions, such as planting trees and reforestation projects. It has been practised before technology-based solutions. These methods are challenging to track, and it is not easy to measure how much carbon is captured exactly.
Both solutions have great potential for the future and in an ideal world, both should be implemented. As companies, research institutions, and government agencies are working on R&D, technology-based carbon removal will become more scalable and nature-based solutions easier to track and measure.
ReCarbn has started a blog to help guide new players in the field of Direct Air Capture and how it fits into the world of carbon removal.
Subscribe to our newsletter!